Traditionally, storage and security are separate disciplines in the IT department. Although the two teams have some overlapping concerns in the data center and work together on some projects, they are very different from each other.

Traditionally, storage and security are separate disciplines in the IT department. Although the two teams have some overlapping concerns in the data center and work together on some projects, they are very different from each other.
Now this model is changing. The continuing security breaches of well-known companies such as Sels, Delta Airlines, Panera Bread, Saks Fifth Avenue, Lord & Taylor, MyFitnessPal, Orbitz, and FedEx have made corporate IT leaders very concerned about the risks they face.
Many people are using DevSecOps, and this approach can make everyone in the organization responsible for security. For storage professionals, this means more attention to data storage security.
What is data storage security?Data storage security is a subset of the IT security domain and is specifically designed to protect storage devices and systems.
The Storage Network Industry Association (SNIA) dictionary provides data storage security definitions:
Storage Security: Apply physical, technical, and administrative controls to protect storage systems and infrastructure and the data stored in them. Storage security focuses on protecting data (and its storage infrastructure) against unauthorized disclosure, modification, or destruction while ensuring the availability of authorized users. These controls may be preventive, investigative, corrective, deterrent, restorative or compensatory.
SNIA also pointed out that secure storage "may also be the last line of defense against the adversary, but only if the storage managers and administrators spend time and energy to implement and activate the available storage security controls."
For storage managers and administrators, ensuring correct data storage security is a careful balancing act. They must weigh the three main issues covered by the acronym CIA: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. They must protect sensitive data from unauthorized users. They must ensure that the data in the system is reliable and that everyone in the organization who needs to access the data can use it.
At the same time, they need to be very aware of the cost and the value of the data. No one hopes that data storage security systems will ultimately be more expensive than the data they protect. However, organizations also need to have a sufficiently strong security system for protection. This requires potential attackers to spend more time and resources than the ultimate value of the data.
Data Security and Data ProtectionStorage security and data security are closely related to data protection. Data security mainly includes preventing the disclosure of private information to unauthorized persons. It also includes protecting data from other types of attacks, such as ransomware that blocks access to information or attacks that alter the data, making it unreliable.
Data protection is more concerned with ensuring that data remains available after a vicious incident, such as failure of a system or component, or even a natural disaster.
In order to ensure the reliability and availability of information, as well as the need to recover from any events that may threaten the organization of data, the common needs of both data security and data protection overlap. Storage professionals often find themselves dealing with data security and data protection issues at the same time, and adopting some of the same best practices can help solve both problems.
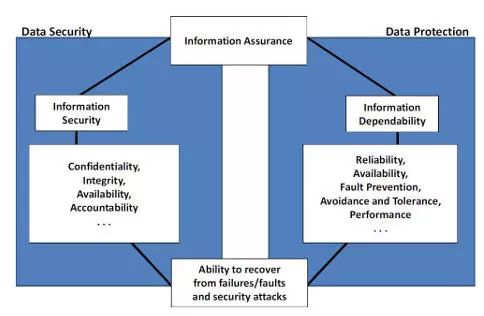
Data security and data protection are obviously overlapping issues
Key drivers for data storage securitySome recent trends are increasing companies’ interest in data security. They include the following:
• Data growth - According to research firm IDC, the amount of data stored in computer systems worldwide has roughly doubled every two years. For businesses, this means constantly adding new storage devices to meet business needs. As storage increases, they become more valuable as a target and are more difficult to protect.
• Growth in cyber attacks – The Verizon 2018 data breach investigation report showed that in 2017, 53,000 security incidents were discovered, including 2,216 data breaches, which was only a small part of the actual incidents in the organization. A recent report released by the British government agency shows that there have been more cyber attacks in 2017 than in any other year. Almost every day such news appears in the news, which makes companies worry about their own security situation.
• The cost of data leakage - Data recovery costs are very high. The survey conducted by the Poronmont Institute on data leakage costs in 2017 found that in the security incidents that occurred in 2017, the average loss per incident for companies that had violated the regulations was approximately US$3.62 million. These costs can be used to improve data security. The strong pressure.
• Increased data value - Due to the rise of big data analytics, companies are more aware of the value of data than ever before. According to research firm Gartner, the market for big data analytics has grown by 63.6% in recent years. By 2020, companies may spend $22.8 billion to purchase tools to help them find valuable data insights. However, in order for the analysis to prove useful, companies need to be able to ensure the authenticity of the data, which means that companies will invest more in security.
• Borderless Networks - Due to the development of emerging technologies such as cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), companies now have more and more extensive data distribution than ever before. Enterprise networks no longer have the rigid advantages that organizations can use to define and protect firewalls. Instead, they must rely more heavily on defense in depth, including storage security to protect their information.
• Regulations - Government departments are increasingly interested in data security and have therefore developed stronger laws. The EU's General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) will take effect on May 25, 2018, forcing companies operating globally to take stronger measures to protect customer privacy and at the same time affect storage security.
• Requires Business Continuity - 2017 was a record year for natural disasters in the United States, highlighting the need for business continuity and disaster recovery capabilities. This has driven the need for secure backups and other storage security technologies.
• DevSecOps Methodology - According to research firm Forrester, 63% of organizations have implemented DevOps, and another 27% plan to do so. With the development of DevOps, more and more companies are becoming more and more interested in it. DevSecOps integrates security into the methods and spreads security responsibilities throughout the organization, including the data storage team.
Storage System Vulnerabilities
Another important driver of data storage security is the inherent vulnerability of storage systems. They include the following:
• Lack of encryption - Although some high-end NAS and SAN devices include automatic encryption, many products on the market do not include these features. This means that organizations need to install separate software or encryption devices to ensure that their data is encrypted.
• Cloud Storage - More and more companies are choosing to store some or all of their data in the cloud. Although some people think that cloud storage is more secure than on-premise storage, cloud computing increases the complexity of the storage environment and often requires storage personnel to learn new tools and implement new procedures to ensure that data is fully protected.
• Incomplete data destruction - When you delete data from your hard disk or other storage media, it may leave traces that could cause unauthorized persons to recover the information. Storage managers and managers need to ensure that any data removed from storage is overwritten so that it cannot be recovered.
• Lack of physical security - Some organizations do not pay enough attention to the physical security of their storage devices. In some cases, they did not consider that insiders (such as employees or members of the cleaning team) may be able to access physical storage devices and extract data to bypass all well-planned network-based security measures.
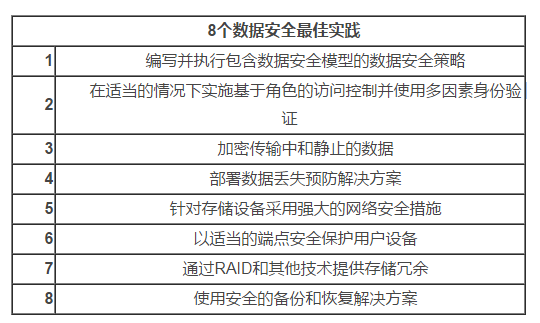
Data Security Best Practices
In order to address these technological trends and address the inherent security vulnerabilities of its storage systems, experts recommend that organizations implement the following data best security practices:
1. Data Storage Security Policy - Businesses should develop written policies that specify appropriate levels of security for the different types of data they own. Obviously, public data requires much less security than restricted or confidential data. Organizations need appropriate security models, processes and tools to implement appropriate protection measures. These policies also include details of the security measures that should be deployed on the organization's storage devices.
2. Access Control - Role-based access control is a prerequisite for secure data storage systems. In some cases, multi-factor authentication may be appropriate. Administrators should also make sure to change any of the default passwords on their storage devices and force users to use strong passwords.
3. Encryption - Data should be encrypted both during transmission and when it is stationary in the storage system. Storage administrators also need a secure key management system to track their encryption keys.
4. Data Loss Prevention - Many experts believe that encryption alone is not sufficient to provide comprehensive data security. They suggest that organizations also deploy Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions to help find and stop any ongoing attacks.
5. Strong network security - Storage systems do not exist in a vacuum, they should be surrounded by powerful network security systems, such as firewalls, anti-malware protection, security gateways, intrusion detection systems, and possibly advanced analysis and Machine learning security solutions. These measures should prevent most cyber attackers from gaining access to storage devices.
6. Strong Endpoint Security - Similarly, organizations need to ensure they have appropriate security measures on personal computers, smart phones, and other devices that access stored data. These endpoints (especially mobile devices) can become a weak link in the organization's cyber attacks.
7. Redundancy - Redundant storage, including RAID technology, not only helps increase availability and performance, but can also help organizations mitigate security incidents in certain situations.
8. Backup and Recovery - Some successful malware or ransomware attacks completely disrupt the corporate network so the only recovery method is to restore from backup. Storage managers need to ensure that their backup systems and processes are suitable for these types of events and for disaster recovery purposes. In addition, they need to ensure that the backup system has the same level of data security as the main system.
Butt Connector,Lugs Insulated Female Connectors,Insulated Female Connectors,Non-Insulated Spade Terminals Wire Connector
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.longyicopperterminals.com