NFC English full name Near Field CommunicaTIon, short-range wireless communication. It is a wireless technology initiated by Philips and jointly promoted by famous manufacturers such as Nokia and Sony.
NFC evolved from the integration of contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) and interoperability technologies, combining inductive readers, inductive cards and point-to-point functions on a single chip to identify and data with compatible devices over short distances. exchange. Originally a simple merger of RFID technology and network technology, this technology has evolved into a short-range wireless communication technology, and the development trend is quite rapid.
Different from RFID, NFC has the characteristics of two-way connection and identification. It works in the frequency range of 13.56MHz and the working distance is about 10 centimeters. NFC technology promotes standardization under the ISO 18092, ECMA340 and ETSI TS 102 190 frameworks, and is also compatible with the widely used ISO 14443 Type-A, B and Felica standard contactless smart card infrastructure.
The NFC chip is installed on the mobile phone, and the mobile phone can realize small electronic payment and read information of other NFC devices or tags. NFC's short-range interaction greatly simplifies the entire authentication process, making it easier, safer, and clearer for electronic devices to access each other. Through NFC, computers, digital cameras, mobile phones, PDAs and other devices can be connected wirelessly conveniently and quickly, thus enabling data exchange and services.
Second, NFC development history and application2.1 History of NFC development
On March 18, 2004, in order to promote the development and popularization of NFC, NXP (formerly Philips Semiconductors), Sony and Nokia created a non-profit industry association, the NFC Forum, to promote the implementation and standardization of NFC technology and ensure equipment. Collaborate with the service. As of 2007, the NFC Forum has more than 100 members worldwide, including: MasterCard International, Panasonic Electronics, Inc., Microsoft, Motorola, NEC, Renesas Technology, Samsung, Texas Instruments, and Visa. International organizations. In July 2006, Fudan Microelectronics became the first Chinese company to join the NFC Alliance. Later, Tsinghua Tongfang Microelectronics also joined the NFC Forum.
In June 2006, NXP, Nokia, China Mobile Xiamen Branch and “Xiamen Yitong Card†launched NFC testing in Xiamen. This cooperation is the first test of NFC mobile payment in China. In August 2006, Nokia and UnionPay Business Corporation announced the launch of a new NFC test in Shanghai. This is the second NFC pilot project in China after Xiamen and the first NFC air download test in the world. The NFC phones used in the tests were all NOKIA 3220.
In March 2007, the European Commission and the Information Society Technology (IST) project jointly invested, and a number of companies, universities and users jointly organized the Pan-European Union to develop an open architecture to further develop and deploy close-range wireless communications. (NFC) technology and promote its application in mobile phones. The project, titled "NFC Application in Warehousing Logistics and Payments (StoLPaN)", aims to develop an open commercial and technical framework for mobile devices, NFC-based services. These architectures will exceed the limitations of handset types and service nature, driving the deployment of NFC-based mobile applications across a wide range of industry markets.
In 2007, Nokia launched its first business phone with NFC technology. The NFC Forum then holds a technical competition each year to reward ideas that promote NFC technology. Since then, many countries around the world have begun testing NFC products. Currently, more than 100 NFC technology development projects are underway worldwide. As with any other new technology, the market popularity of NFC technology needs to be improved. But in time, NFC technology will undoubtedly enter the ranks of mainstream applications.
2.2 NFC application
Contactless payment
Transportation
medical health
Smart goal
social media
Third, the technical principle and comparison3.1 Technical principles
NFC-enabled devices can exchange data in active or passive mode.
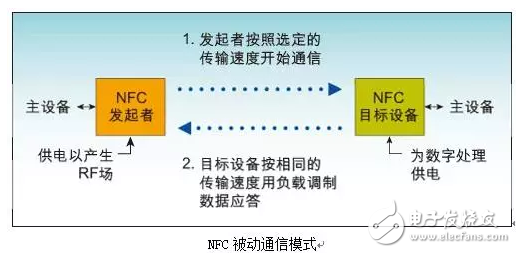
In passive mode, a device that initiates NFC communication, also known as an NFC originating device (master device), provides an RF-field throughout the communication process.
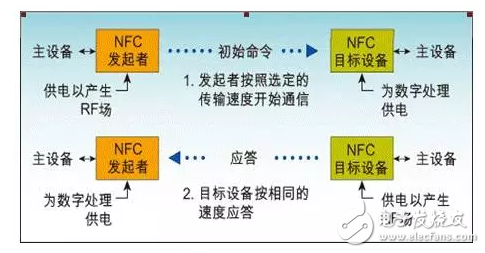
In active mode, each device must generate its own RF field when it wants to send data to another device. As shown in Figure 1, both the initiating device and the target device generate their own RF fields for communication. This is the standard mode for peer-to-peer network communication and allows for very fast connection settings.
2D Barcode Scanner
Features
Material:TPU+PC, more rugged than ABS + PC, more stronger fall resistance
Charging Base:charging base not only charge ring scanner but also can be regarded as a bluetooth adapter to connect ring scanner with PC
Compatible With Most Operation System:We can provide the software(Bluetooth input method)for Windows and Android, By the way, there are corresponding SDK
Applicable scope
1.Comercial POS system(Supermarkets
2.Warehousing and logistics
3.Libraries
4.Banks and Telecom
5.Transportaion
6.Postal service
7.Industrial and manufacturing management
2D Barcode Scanner,Data Matrix Barcode Scanner,2D Barcode Scanner Usb,1D 2D Scanner
ShengXiaoBang(GZ) Material Union Technology Co.Ltd , https://www.sxbgz.com