1 Overview of the development of the Internet of Things
1.1 The concept and development of the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things is a new technology system that is a combination of multiple information technologies. It is called the third wave of the world information industry after computers and the Internet. Things (Internet of Thlngs, IoT) is a radio frequency identification (RFID), sensor networks, global positioning systems, laser scanners and other information sensing device, according to the agreement, and the items connected to the Internet, information exchange and communication A network that enables intelligent identification, location, tracking, monitoring, and management of items and triggers corresponding events. The Internet of Things realizes the interconnection and interaction between objects and objects through a short-range wireless self-organizing network based on the "object-object" communication mode (M2M).
The original concept of the Internet of Things originated from the Radio Frequency Identification System (RFID) proposed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1999. RFID connects the object and the object with radio frequency identification communication technology to realize the intelligent identification of the object, and realizes the remote location, monitoring and management of the object by connecting to the Internet. At the same time, with the maturity of wireless sensor network technology, the Internet of Things architecture based on RFID technology and sensor network technology has emerged. After the Internet realizes the remote interaction between people, the Internet of Things will realize the remote interaction between things and things, people and things. At present, the development of the Internet of Things has been identified as the focus of national strategy in all major countries around the world. Since 2008, has developed into a number of research institutions worldwide consisting of Auto-ID Lab jointly organized the "Internet of Things" International Convention. June 18, 2009, the European Commission published an "Internet of things - an acTIon plan for Europe", describes the prospects for the development of things in the world for the first time the system put forward the development and management vision of things, And proposed 12 actions to ensure the accelerated development of the Internet of Things. The US National Intelligence Council (NIC) published the "Key Technologies for Potential Impacts on US Interests in 2025" report, which listed the Internet of Things as one of six key technologies. China also put forward the transformation of the use of Internet of Things technology to promote economic development in the "2010 Government Work Report". The Internet of Things will become one of the strategic pillars of national economic and technological development.
1.2 Internet of Things Architecture
According to the Internet of Things architecture (Figure 1) given by the EU's Seventh Framework Project CASAGRAS2, the Internet of Things should have four levels: 1 perception layer. In the sensing layer, various objects form a local network by self-assembly by embedding sensing devices such as RFID and wireless sensors, acquire information of their own state or surrounding environment, and transmit information to the transport layer through the access network. In some systems, the perception layer can perform some preliminary processing and response based on the collected information. 2 transport layer. Through the integration of various telecommunication networks (including broadband wireless networks, fiber-optic networks, cellular networks, and various private networks) with the Internet, the information of the sensing layer is accurately received in real time, and the information is sent to the processing layer for calculation processing. 3 processing layer. Using the resources of the Internet, cloud computing provides data storage, processing, decision-making, control and other functions to achieve deep interconnection and interaction between global objects. 4 Application layer, establish various specific applications in different fields such as agriculture, military, environmental disaster monitoring, logistics supply chain.
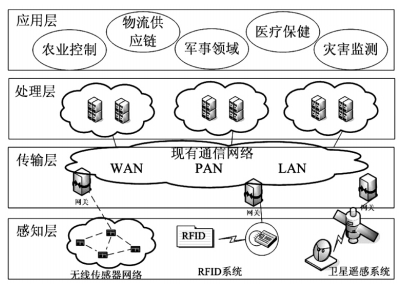
Figure 1 Internet of Things Architecture
1.3 Application of Internet of Things in Agriculture
China's agriculture is in the transition period from traditional agriculture to modern agriculture. Network information technology will play a unique and important role in this period, and it will provide an unprecedented opportunity for modern agricultural development. The Agricultural Internet of Things can embed sensors into various objects such as agricultural machinery, land, and irrigation systems, and then integrate “things†with the Internet to implement real-time management and control through intelligent analysis. In this way, humans can manage agricultural production in a more refined and dynamic manner, improve resource utilization and productivity levels, and promote sustainable development.
The application scope of the Internet of Things in modern agriculture is mainly reflected in the following aspects: (1) The establishment of agricultural precision control system using wireless sensor networks. Conduct crop field and greenhouse environmental control and information feedback, use it to detect environmental information of crops, monitor data such as temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind speed, crop growth, etc., and process this information to make decisions for agricultural experts. Develop farmland variable work prescriptions to provide the main data sources and parameters; also automatically trigger related behaviors, such as intelligent irrigation or automatic temperature adjustment to ensure a good growth environment for crops. (2) Apply RFID technology to establish a tracking and traceability system for the food supply chain of modern aquaculture. RFID technology is used for individual identification of livestock and poultry, and combined with wireless sensor network, handheld mobile device and PC database technology to build RFID culture management information system to track the production, processing, wholesale and retail of pork products. Realize effective traceability of livestock and poultry data and share data and business. (3) Agricultural sensors can also be applied to mobile information equipment manufacturing industry, agricultural resource management, agricultural information network service industry, agricultural automatic identification technology and equipment industry, agricultural fine operation equipment industry and agricultural product logistics industry, to achieve agricultural production automation and intelligence. .
2 Development of key technologies in agricultural internet of things
In recent years, the key theories, technologies and applications of the Internet of Things have become the research hotspots of the industry and academia, covering the whole process from information acquisition, transmission, storage, processing to application. The Internet of Things should have three characteristics: one is comprehensive perception, that is, the use of RFID, sensors, etc. to obtain information of objects anytime and anywhere; the second is reliable transmission, through the integration of various telecommunication networks and the Internet, the object information is accurately transmitted in real time. The third is intelligent processing, using cloud computing, sea computing, fuzzy recognition and other intelligent computing technologies to analyze and process massive amounts of data and information, and implement intelligent control of objects. The key technologies in the agricultural Internet of Things are also mainly focused on sensor network technology, identity technology, communication technology, and intelligent processing technology.
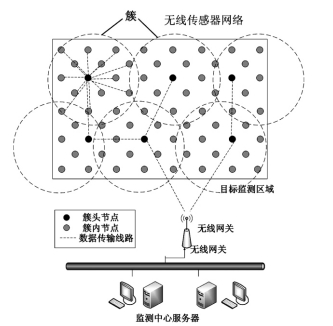
Figure 2 Precision Agricultural Control System
2.1 Sensor Network Technology
Wireless sensor networks are an important means of sensing things and transmitting data in the Internet of Things, and can constitute important antennas and nerves of the Internet of Things. A wireless sensor network is a multi-hop self-organizing network system composed of a large number of micro-sensor nodes deployed in a monitoring area. The purpose is to cooperatively perceive, collect and process the perceptual objects in the network coverage area. Information and send it to the observer. Wireless sensor networks have been widely used in the field of agricultural information, such as precision agriculture, intelligent expert management systems, and remote monitoring.
A precise agricultural control system based on wireless sensor networks enables real-time online monitoring of the environment. The system consists of a wireless sensor network, a wireless gateway and a monitoring center (Figure 2). Sensor nodes distributed in the monitoring area collect environmental data, including soil temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind speed, and crop growth. The type of sensor can be selected according to the farmland parameters to be monitored, such as temperature and humidity sensors, atmospheric pressure sensors, and light intensity sensors. The sensor node forms a sensor network in a ZigBee ad hoc network manner and transmits data to the wireless gateway through one-hop or multi-hop wireless communication. The wireless gateway receives the data transmitted by the sensor node and transmits the data to the monitoring center through other external networks (Internet or GPRS). The monitoring center is responsible for issuing query requests for environmental indicators to the target monitoring area, and analyzing and processing the collected data to provide the main data sources and parameters for agricultural experts to make decisions and formulate farmland variable operation prescriptions.
At present, comprehensive application demonstration bases such as facility agriculture digital technology, field crop digital technology and digital agricultural integration technology have been established in many provinces. Some advanced agricultural sensors are also used in experimental applications, such as electrochemical ion sensors for rapid detection of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and heavy metals in soils; biosensors for rapid detection of avian influenza and detection of commercial pathogenic bacteria; Gas sensor for food quality, gas pollution, emissions monitoring, etc.
In the future, agricultural sensor technology will develop in the direction of miniaturization, low power consumption and high reliability. Can the cost of building a sensor network be reduced, the power consumption of the sensor can be reduced, and the life cycle of the sensor network can be extended? The key to widespread adoption. In addition, how to improve the reliability of the sensor network will also be the focus of research. The existing wireless sensor network spatial range query processing algorithm has large energy consumption, and when the node fails, the query processing process is easily interrupted, and the query result cannot be returned. Liu Liang et al. proposed an energy efficient algorithm ESA, which reduces the number of data messages sent by sensor nodes and reduces the energy consumed by the algorithm to distribute query messages. At the same time, an algorithm for recovering the query processing process by using node redundancy is designed to reduce the probability that the algorithm will be interrupted due to node failure.
2.2 Identification Technology
The Internet of Things requires individual identification of a large number of objects in the sensing layer, namely, identification technology. RFID RFlD (Radio Frequency IdenTIficaTIon) tagging technologies has become the main object of the IOT aware identification, and by combining the Internet, communications, and other techniques to achieve item tracking and sharing of information worldwide.
RFID is a non-contact automatic identification technology that automatically identifies target objects and acquires relevant data through radio frequency signals. The identification process requires no human intervention. The RFID system consists of three parts: an electronic tag, a reader and a central information system. The electronic tag can be divided into an active electronic tag powered by a self-contained battery and a passive electronic tag without a self-contained power supply. The working principle of the RFID system (Fig. 3) is: after the electronic tag enters the range covered by the RF signal emitted by the reader, the passive electronic tag transmits the product information stored in the chip by the energy obtained by the induced current. The source electronic tag actively transmits a signal of a certain frequency to transmit its own product information. When the reader reads the information and decodes it, it sends the information to the central information system for data processing.
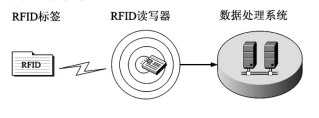
Figure 3 RFID working principle diagram
The application of RFID technology in the supervision of agricultural product quality and safety has become more and more popular, and research on the quality and safety traceability of agricultural products has made some progress. The application of RFID technology in agricultural product traceability system can penetrate into all aspects of agricultural raw materials, product processing and logistics sales. In the breeding of agricultural and livestock products, RFID technology can be used to mark Chinese animals, record and control plague, etc., mainly include collar electronic tags, button-type electronic ear tags, ear-injected electronic tags, and rumen electronic tags placed through the esophagus. Ways to record animal information. Yan Liwei proposed and established a cow identification system based on radio frequency identification technology. The system uses a rumen-type animal electronic logo to create a permanent digital file for each cow, implements a livestock and a standard, and uses the RFID technology and the communication technology between the single-chip computer and the PC to remotely store the electronic tags of the dairy cow information. Distance identification enables timely monitoring and management of each cow. The research results show that the RFID system reader has a reading rate of 100% and a reading distance of more than 8m. Ren Shougang and others designed a meat sales tracking and tracing system based on radio frequency identification technology, including tracking system and traceability system. The tracking system tracks the meat information attached to the RFID tag through the product electronic code system on the sales node. The traceability system uses the Object Name Resolution Service (ONS) server to find the address of the meat sales related node entity markup language (PML) server, thereby obtaining the circulation information of the meat, and then combining the information with the geographic information of the node. Geographic Information System (GIS) software for visual display. Luo Qingyi and others used UHF radio frequency identification technology to design RFID tags suitable for pig carcasses, developed an electronic tag online reading and writing system, and realized the RFID identification and long-distance automatic reading of pig carcasses in the pig slaughtering line. Through the automatic collection of pig earmarking ear tag information collection, RFID tag information and the intranet traceability data recording system of the slaughterhouse, the reliable collection, transmission and processing of the pig slaughter identification information in the traceability of the pig slaughtering process are realized.
With the development of the Internet of Things, RFID technology faces challenges in terms of cost issues, recognition accuracy, operational environment impact, global standardization of coding systems, privacy and security. At the same time, the development of highly reliable and more advanced identification technologies, such as the combination of DNA biometric identification technology and Internet of Things technology, will be a hot topic of research.
2.3 Communication technology
The communication technologies in the Internet of Things can be roughly divided into two categories according to their functions: one is wireless communication technology, that is, the communication between objects in the short-range wireless self-organizing network in the Internet of Things, such as radio frequency identification technology RFID, ZiBee, a low-power short-range wireless networking communication technology commonly used in WSN, in addition to UWB, Wifi, Wimax, Bluetooth, 6LoWPAN, etc.; one type of network access technology from wireless communication to traditional telecommunication networks or the Internet It includes cellular networks such as GSM and TD-SCDMA, private wireless networks such as WLAN and WPAN, and various networks such as the Internet. The Internet access of the Internet of Things is done through the gateway. The wireless communication technology in the Internet of Things will continue to meet the requirements of miniaturization, low power consumption, and high reliability. For example, low-power RF chips, on-chip antennas, and millimeter-wave chips will become hot spots.
2.4 Intelligent Processing Technology
For the massive data collected by the IoT awareness layer, the processing layer will analyze and process the data and information. The “cloud†of cloud computing is at the processing layer, and the data center is mainly used to provide services to implement intelligent control of objects. Cloud computing is an emerging computing model that manages and schedules a large number of computing resources connected by networks to form a computing resource pool to serve users on demand. Cloud computing mainly uses data mining, pattern recognition, search engine, data analysis, artificial intelligence and other technologies to provide high-capacity, high-performance decision-making and processing control functions to the Internet of Things. Currently, cloud computing faces the challenge of security and standardization. Since the application system is deployed on the public cloud and contains a large amount of user sensitive information, how to design different scenarios and different levels of privacy protection technology will be a hot issue for the research of IoT security technology. At present, there is no unified standard for cloud computing. There is a lack of interoperability between different clouds. When users migrate from one cloud computing environment to another, they face enormous difficulties. Establishing open cloud computing standards as soon as possible will ensure the sustainable and healthy development of China's cloud computing industry.
3 Summary
The Internet of Things is a new technology system that is a combination of multiple information technologies. It is called the third wave of the world information industry after computers and the Internet. The application of agricultural Internet of Things technology is the need of modern agricultural development and an important indicator of the future development level of agriculture. It will be the direction of future agricultural development. Based on the Internet of Things architecture, this paper analyzes the key technologies of sensor network technology, identity recognition technology, communication technology and intelligent processing technology in agricultural internet of things, and points out its challenges and development directions. The development of agricultural Internet of Things will definitely bring a new reform to modern agriculture, improve the quantity and quality of global agricultural products, increase farmers' income, enhance food safety, and realize agricultural automation and intelligence.
For more information on medical electronic design, please pay attention to the topic "Communication of the core technology of the Internet of Things"
1000W Solar Generator
Super Green Energy Portable Solar Generator Battery Energy Storage System USB Power Station for Outdoor Picnic

1000 Solar Generator,All In One Solar Generator,Outside Home Off grid Portable Solar Generator
suzhou whaylan new energy technology co., ltd , https://www.nbwhaylan.com