Over the years, as analog content has gradually transitioned to digital content, new video surveillance application models have emerged. The corporate security team and information technology team need to continue to strengthen cooperation to jointly design solutions that can meet more complex requirements. As an example, although approximately 95% of video surveillance I / O operations are write operations, most enterprise storage systems are designed to speed up read speeds, which are often constrained by data protection factors.
Writing applications are different from traditional read / write systems in terms of specifications. First, the degree of risk associated with the loss of video footage (footage loss) is the most important determinant that customers of such storage applications need to consider. Other factors to be concerned about include storage capacity, resolution and data protection.
Which RAID level to choose depends largely on the final priority of the above factors. In order to obtain the best storage solution, we need to fully understand which level the customer belongs to and the available budget size.
Source: Pelco Technical White Paper: "Improving the reliability of video surveillance storage systems while reducing costs"
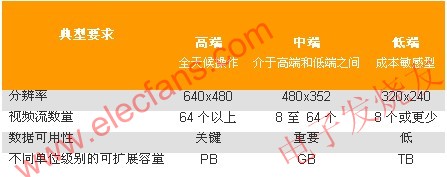
High-end applications
High-end applications need to run around the clock. The risk caused by the loss of video clips is extremely high, and institutions that use high-end applications (airports, prisons, etc.) often need to meet strict specifications to ensure that the data is intact. Since PB-level (rather than GB-level) data is often required for long-term storage, large storage capacity requirements are critical. The number of video streams is also high. For example, a system with 100 cameras can generate more than 30 TB of data per week. High-end applications usually require the highest possible resolution, so the bit rate is also high. In addition, because the content is difficult to copy once it is lost, no matter how high the cost is, protecting the hard disk data is very important. Another factor to consider in this type of environment is that the storage system must be able to save video streams in any array. This also includes ensuring a minimum performance level in degraded mode or during reconstruction.
RAID 6 is the best choice to ensure 24/7 operation. It provides dual parity protection against dual drive failures and allows administrators sufficient time to replace failed drives before data is damaged.
Mid-range applications
For organizations (enterprises, schools, etc.) that use mid-range applications, the risk associated with video stream capture failures is relatively low, but there is still a high capacity requirement to meet the requirements of on-demand archiving and reference video clips. Data quality requirements may vary, some may require higher resolutions, and some may only require lower video quality. It is still very important to avoid data protection and drive failures, but the difference from high-end applications is that mid-end applications can accept a small amount of frame loss when rebuilding the array. Of course, this phenomenon should be avoided as much as possible.
If the archiving requirements need to support high data availability, then RAID 6 will be the best choice for customers. If the customer has enough IT personnel on site to replace the drive, or it is not necessary to ensure long-term 24/7 work, RAID 5 is more suitable, which helps to obtain higher net storage capacity compared to RAID 6.
Low-end applications
Low-end products are mainly concerned with cost. Even if the frame is lost, there is not much risk, and it can be rewritten every day, so the capacity requirement is low. Organizations using such low-end applications (retailers, small offices, etc.) can use images with lower resolutions and do not need to worry about data protection when the drive fails.
RAID 0 is the lowest cost RAID level that can achieve the highest performance with the least number of drives and provide the maximum net storage capacity for the system. However, if one of your drives fails, using RAID 0 will result in data loss. If the customer needs data protection and the budget is tight, consider using other levels such as RAID 10 or 5.
Choose the appropriate RAID level
Based on the above analysis, we can see that high-end applications need to ensure 24/7 operation, and RAID 6 is the best RAID technology that can meet this high availability requirement. The specifications of mid-range applications vary, so RAID 5 is usually a good choice. For most cost-sensitive low-end applications, RAID 0 is an appropriate choice that we should consider, especially if it allows daily rewrites. If you need data protection technology, you can choose RAID 5 and 10.

LSI 6Gb / s SATA + SAS configuration and test results
To help users choose components for customer video surveillance applications, LSI has configured and conducted some tests to show how to achieve the desired level of performance for users to consider when considering storage solutions.
System Configuration
• Supermicro X8DTL-6F server
• Dual Xeon CPU
• 2x2GB DRAM
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise EdiTIon, Service Pack 2
• LSI 3ware 9750-8E (driver version is 5.01.00.016, firmware version is FH9X 5.12.00.006)
• LSI 620J connected to two x4 multi-wire cables (with 6Gb expander backplane)
• 24 Seagate 6Gb SAS drives (Model: ST973352SS)
Test configuration
• The depth of each worker queue using IOmeter is 1
• 256 KB stripe
• 100% sequential write
• Write cache supports the best results for each RAID type (WT / WB)
• RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6
• Run time 2 minutes
• Ramp up time 30 seconds

Radio modems are dedicated to transfer data between two or more locations. GrandComm`s radio modems operate in VHF and UHF frequency band and can cover a distance of over 50 kilometers. The radio modems can provide programmable serial baud rates from 1200bps to 115200bps.
GrandComm`s radio modem products are designed to industrial standards and well-suited for SCADA, telemetry and process control applications in wireless environment. The radio modem can communicate data of remote control signals, telemetry signals from a transducer, computer`s RS232 port, GPS position signals, or a digital terminals.
Radio Modem
Radio Modem,RF Modem,Data Radio Modem,Serial Radio Modem
Shenzhen PuFang Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.hytelus.com